
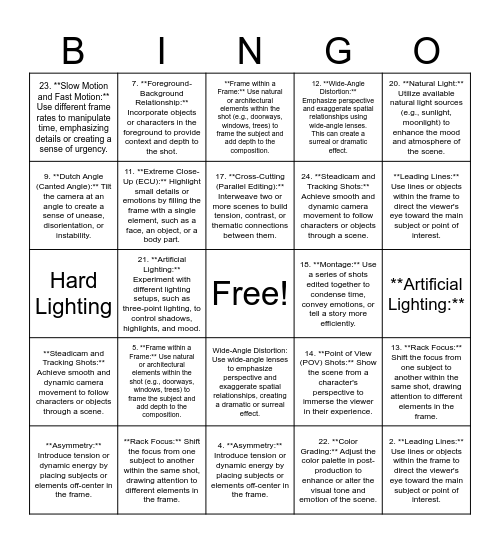
This bingo card has a free space and 51 words: 1. **Rule of Thirds:** Divide the frame into a 3x3 grid, and place key elements along the gridlines or at the intersections to create a visually pleasing balance., 2. **Leading Lines:** Use lines or objects within the frame to direct the viewer's eye toward the main subject or point of interest., 3. **Symmetry:** Create balanced and harmonious compositions by centering the subject or using symmetrical elements in the frame., 4. **Asymmetry:** Introduce tension or dynamic energy by placing subjects or elements off-center in the frame., 5. **Frame within a Frame:** Use natural or architectural elements within the shot (e.g., doorways, windows, trees) to frame the subject and add depth to the composition., 6. **Depth of Field:** Adjust the aperture to control the depth of field, allowing you to emphasize or de-emphasize specific elements within the frame., 7. **Foreground-Background Relationship:** Incorporate objects or characters in the foreground to provide context and depth to the shot., 8. **High and Low Angles:** Change the camera's height to create different perspectives and convey power dynamics or emotions. A low angle can make a subject appear dominant, while a high angle can make them seem vulnerable., 9. **Dutch Angle (Canted Angle):** Tilt the camera at an angle to create a sense of unease, disorientation, or instability., 10. **Long Shot (Establishing Shot):** Use wide-angle shots to establish the setting and context before zooming in for closer shots., 11. **Extreme Close-Up (ECU):** Highlight small details or emotions by filling the frame with a single element, such as a face, an object, or a body part., 12. **Wide-Angle Distortion:** Emphasize perspective and exaggerate spatial relationships using wide-angle lenses. This can create a surreal or dramatic effect., 13. **Rack Focus:** Shift the focus from one subject to another within the same shot, drawing attention to different elements in the frame., 14. **Point of View (POV) Shots:** Show the scene from a character's perspective to immerse the viewer in their experience., 15. **Over-the-Shoulder (OTS) Shots:** Frame a character's dialogue or interaction from behind another character's shoulder to establish spatial relationships and convey reactions., 16. **Match Cut:** Transition between two shots by matching elements, such as shape, color, or movement, to create continuity or emphasize a thematic connection., 17. **Cross-Cutting (Parallel Editing):** Interweave two or more scenes to build tension, contrast, or thematic connections between them., 18. **Montage:** Use a series of shots edited together to condense time, convey emotions, or tell a story more efficiently., 19. **Silhouettes:** Create striking images by placing the subject in front of a bright background, allowing only their outline to be visible., 20. **Natural Light:** Utilize available natural light sources (e.g., sunlight, moonlight) to enhance the mood and atmosphere of the scene., 21. **Artificial Lighting:** Experiment with different lighting setups, such as three-point lighting, to control shadows, highlights, and mood., 22. **Color Grading:** Adjust the color palette in post-production to enhance or alter the visual tone and emotion of the scene., 23. **Slow Motion and Fast Motion:** Use different frame rates to manipulate time, emphasizing details or creating a sense of urgency., 24. **Steadicam and Tracking Shots:** Achieve smooth and dynamic camera movement to follow characters or objects through a scene., 25. **Handheld Camera:** Create a sense of immediacy, chaos, or intimacy by shooting without a tripod or stabilizer., **Rule of Thirds:** Divide the frame into a 3x3 grid, and place key elements along the gridlines or at the intersections to create a visually pleasing balance., **Leading Lines:** Use lines or objects within the frame to direct the viewer's eye toward the main subject or point of interest., **Symmetry:** Create balanced and harmonious compositions by centering the subject or using symmetrical elements in the frame., **Asymmetry:** Introduce tension or dynamic energy by placing subjects or elements off-center in the frame., **Frame within a Frame:** Use natural or architectural elements within the shot (e.g., doorways, windows, trees) to frame the subject and add depth to the composition., **Depth of Field:** Adjust the aperture to control the depth of field, allowing you to emphasize or de-emphasize specific elements within the frame., **Foreground-Background Relationship:** Incorporate objects or characters in the foreground to provide context and depth to the shot., **High and Low Angles:** Change the camera's height to create different perspectives and convey power dynamics or emotions. A low angle can make a subject appear dominant, while a high angle can make them seem vulnerable., **Dutch Angle (Canted Angle):** Tilt the camera at an angle to create a sense of unease, disorientation, or instability., **Extreme Close-Up (ECU):** Highlight small details or emotions by filling the frame with a single element, such as a face, an object, or a body part., **Rack Focus:** Shift the focus from one subject to another within the same shot, drawing attention to different elements in the frame., **Point of View (POV) Shots:** Show the scene from a character's perspective to immerse the viewer in their experience., **Over-the-Shoulder (OTS) Shots:** Frame a character's dialogue or interaction from behind another character's shoulder to establish spatial relationships and convey reactions., **Silhouettes:** Create striking images by placing the subject in front of a bright background, allowing only their outline to be visible., **Natural Light:** Utilize available natural light sources (e.g., sunlight, moonlight) to enhance the mood and atmosphere of the scene., **Artificial Lighting:**, **Steadicam and Tracking Shots:** Achieve smooth and dynamic camera movement to follow characters or objects through a scene., **Handheld Camera:** Create a sense of immediacy, chaos, or intimacy by shooting without a tripod or stabilizer., Black and White, Flat Lighting, Soft Lighting, Hard Lighting, Negative Space: Leave empty or negative space around your subject to emphasize its importance and create a sense of simplicity or isolation., Reflections: Incorporate reflective surfaces like water, glass, or mirrors to create symmetry, depth, or surreal effects., Wide-Angle Distortion: Use wide-angle lenses to emphasize perspective and exaggerate spatial relationships, creating a dramatic or surreal effect. and Color Theory: Use color harmonies (complementary, analogous, or triadic) to create visual interest and convey emotions in your photographs..
shot coverage | Elements, Principles, Stages of Clay | Film Night Bingo! | Film Style and Framing | Photography Composition Bingo
Share this URL with your players:
For more control of your online game, create a clone of this card first.
Learn how to conduct a bingo game.
With players vying for a you'll have to call about __ items before someone wins. There's a __% chance that a lucky player would win after calling __ items.
Tip: If you want your game to last longer (on average), add more unique words/images to it.