Disaccharides: two mono- saccharides linked together Dehydration synthesis: removes equivalent of a water molecule to link molecular units Poly- saccharides: store energy Cholesterol produces hormones (testosterone & estrogen) Nucleic acids store genetic information Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides Proteins: long chains of amino acids Steroids: carbon- based ring structures Lipids: insoluble in water Enzymes facilitate biochemical reactions Mono- saccharides: simple sugars 20 types of amino acids Phospholipids: cell membrane structure Primary structure: stabilized by peptide bonds Carbohydrates: used for energy and structural support. Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains Hydrolysis: Adds the equivalent of a water molecule to break apart macromolecules Triglycerides: energy storage molecules Tertiary structure: creates polar and non-polar areas in molecule Oligo- saccharides: more than one monosaccharide linked together Secondary structure: stabilized by hydrogen bonds Disaccharides: two mono- saccharides linked together Dehydration synthesis: removes equivalent of a water molecule to link molecular units Poly- saccharides: store energy Cholesterol produces hormones (testosterone & estrogen) Nucleic acids store genetic information Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides Proteins: long chains of amino acids Steroids: carbon- based ring structures Lipids: insoluble in water Enzymes facilitate biochemical reactions Mono- saccharides: simple sugars 20 types of amino acids Phospholipids: cell membrane structure Primary structure: stabilized by peptide bonds Carbohydrates: used for energy and structural support. Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains Hydrolysis: Adds the equivalent of a water molecule to break apart macromolecules Triglycerides: energy storage molecules Tertiary structure: creates polar and non-polar areas in molecule Oligo- saccharides: more than one monosaccharide linked together Secondary structure: stabilized by hydrogen bonds
(Print)
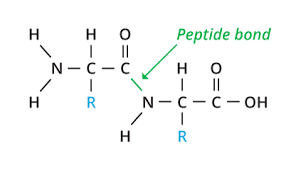
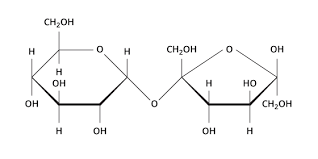
Disaccharides: two mono-saccharides linked together
Dehydration synthesis: removes equivalent of a water molecule to link molecular units
Poly-
saccharides: store energy
Cholesterol produces hormones (testosterone & estrogen)
Nucleic acids store genetic information
Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides
Proteins: long chains of amino acids
Steroids: carbon-based ring structures
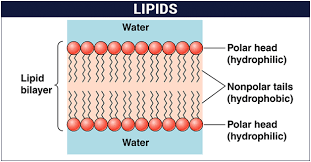
Lipids: insoluble in water
Enzymes facilitate biochemical reactions
Mono-saccharides: simple sugars
20 types of amino acids
Phospholipids: cell membrane structure
Primary
structure: stabilized by peptide
bonds
Carbohydrates: used for energy and structural support.
Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains
Hydrolysis: Adds the equivalent of a water molecule to break apart macromolecules
Triglycerides: energy storage molecules
Tertiary
structure: creates polar
and non-polar
areas in molecule
Oligo-saccharides: more than one monosaccharide linked together
Secondary structure: stabilized by hydrogen bonds