Nodes of Ranvier Vasodilation Anaerobic respiration (animals) virus life cycle Thyroxine Presynaptic neuron NADH Dendrites Cell- mediated immune response Stomata Natural immunity Phospholipid bilayer Endocytosis Hydrophobic Countercurrent flow Cell body (soma) Inflammatory response Secondary immune response golgi apparatus Prokaryotic cell Osmoconformer Oxygen dissociation curve Artificial immunity Self & Non- self recognition (immune response) Glomerulus Hibernation Hypertonic Fluid mosaic model Mitochondria virulence factors Extrinsic protein Exocytosis Active transport Vaccine Primary immune response Action potential Nucleotides Intrinsic protein Agglutination Phosphate head & 2 fatty acid tails Aerobic cellular respiration Hydrophilic lactic acid Nodes of Ranvier (neuron) Innate (non- specific) immune response acquired immune response (T- cell activation) Potassium efflux MHC receptor Insulin Xylem Effector/Plasma cells Light independent reactions B cells TSH Chloroplasts Myelin sheath Active immunity Motor neuron Gas exchange Collecting duct Antibody (variable region) Enzymes Resting membrane potential Hyperthermia ADH Companion cells Glycolipid Sodium- potassium pump Kleptothermy Humoral immune response Adaptive (specific) immune response (vertebrates) Osmosis Homeostasis Mast cell Capillaries SA:V Helper T cells Schwann cells Effectors (muscles and glands) Toxin neutralisation Repolarisation Fatty acids and glycerol Digestive system (Villi) Anaerobic respiration/ fermentation (yeast) ATP Phagocytosis Hypothermia Nephron Moist surface (Lungs) Active site Pathogen Photosynthesis Pholoem Denatured Cilia and Mucus Neurotransmitter Postsynaptic neuron Kreb's cycle Bowman's capsule Antigen Eukaryotic cell Passive immunity Induced- fit & Lock and key theory Afferent impulses (towards CNS) ADP + p Distal convoluted tubule Hyperpolarisation Alveoli Inflammation Large concentration gradient maintained (Lungs) Opsonisation Fish Gills (countercurrent flow) Glycolysis Isotonic acquired immune response (antibody producing B- cells) Negative feedback systems Sieve tubes Memory cells Loop of Henle Histamine Pyruvate NADPH TRH Large SA:V ratio (Lungs) Synapse Water potential Hypotonic Sieve plates Electron Transport Chain Light dependent reactions Proximal convoluted tubule Efferent impulses (away from CNS, to the effector) Sodium influx Transpiration Complement system Antibodies Sensory neuron Lysosome (lysozyme) Osmoregulator Amino acids disease vector (e.g. mosquito - carries the pathogen) Adhesion- cohesion (plants) Glycoprotein Hormones Passive transport Depolarisation Threshold potential (neuron) Sensory receptors (chemo, thermo, photo, mechano, noci) Axon Nodes of Ranvier Vasodilation Anaerobic respiration (animals) virus life cycle Thyroxine Presynaptic neuron NADH Dendrites Cell- mediated immune response Stomata Natural immunity Phospholipid bilayer Endocytosis Hydrophobic Countercurrent flow Cell body (soma) Inflammatory response Secondary immune response golgi apparatus Prokaryotic cell Osmoconformer Oxygen dissociation curve Artificial immunity Self & Non- self recognition (immune response) Glomerulus Hibernation Hypertonic Fluid mosaic model Mitochondria virulence factors Extrinsic protein Exocytosis Active transport Vaccine Primary immune response Action potential Nucleotides Intrinsic protein Agglutination Phosphate head & 2 fatty acid tails Aerobic cellular respiration Hydrophilic lactic acid Nodes of Ranvier (neuron) Innate (non- specific) immune response acquired immune response (T- cell activation) Potassium efflux MHC receptor Insulin Xylem Effector/Plasma cells Light independent reactions B cells TSH Chloroplasts Myelin sheath Active immunity Motor neuron Gas exchange Collecting duct Antibody (variable region) Enzymes Resting membrane potential Hyperthermia ADH Companion cells Glycolipid Sodium- potassium pump Kleptothermy Humoral immune response Adaptive (specific) immune response (vertebrates) Osmosis Homeostasis Mast cell Capillaries SA:V Helper T cells Schwann cells Effectors (muscles and glands) Toxin neutralisation Repolarisation Fatty acids and glycerol Digestive system (Villi) Anaerobic respiration/ fermentation (yeast) ATP Phagocytosis Hypothermia Nephron Moist surface (Lungs) Active site Pathogen Photosynthesis Pholoem Denatured Cilia and Mucus Neurotransmitter Postsynaptic neuron Kreb's cycle Bowman's capsule Antigen Eukaryotic cell Passive immunity Induced- fit & Lock and key theory Afferent impulses (towards CNS) ADP + p Distal convoluted tubule Hyperpolarisation Alveoli Inflammation Large concentration gradient maintained (Lungs) Opsonisation Fish Gills (countercurrent flow) Glycolysis Isotonic acquired immune response (antibody producing B- cells) Negative feedback systems Sieve tubes Memory cells Loop of Henle Histamine Pyruvate NADPH TRH Large SA:V ratio (Lungs) Synapse Water potential Hypotonic Sieve plates Electron Transport Chain Light dependent reactions Proximal convoluted tubule Efferent impulses (away from CNS, to the effector) Sodium influx Transpiration Complement system Antibodies Sensory neuron Lysosome (lysozyme) Osmoregulator Amino acids disease vector (e.g. mosquito - carries the pathogen) Adhesion- cohesion (plants) Glycoprotein Hormones Passive transport Depolarisation Threshold potential (neuron) Sensory receptors (chemo, thermo, photo, mechano, noci) Axon
(Print)
Nodes of Ranvier
Vasodilation
Anaerobic respiration (animals)
virus life cycle
Thyroxine
Presynaptic neuron
NADH
Dendrites
Cell-mediated immune response
Stomata
Natural immunity
Phospholipid bilayer
Endocytosis
Hydrophobic
Countercurrent flow
Cell body (soma)
Inflammatory response
Secondary immune response
golgi apparatus
Prokaryotic cell
Osmoconformer
Oxygen dissociation curve
Artificial immunity
Self & Non-self recognition (immune response)
Glomerulus
Hibernation
Hypertonic
Fluid mosaic model
Mitochondria
virulence factors
Extrinsic protein
Exocytosis
Active transport
Vaccine
Primary immune response
Action potential
Nucleotides
Intrinsic protein
Agglutination
Phosphate head & 2 fatty acid tails
Aerobic cellular respiration
Hydrophilic
lactic acid
Nodes of Ranvier (neuron)
Innate (non-specific) immune response
acquired immune response (T-cell activation)
Potassium efflux
MHC receptor
Insulin
Xylem
Effector/Plasma cells
Light independent reactions
B cells
TSH
Chloroplasts
Myelin sheath
Active immunity
Motor neuron
Gas exchange
Collecting duct
Antibody (variable region)
Enzymes
Resting membrane potential
Hyperthermia
ADH
Companion cells
Glycolipid
Sodium-potassium pump
Kleptothermy
Humoral immune response
Adaptive (specific) immune response (vertebrates)
Osmosis
Homeostasis
Mast cell
Capillaries
SA:V
Helper T cells
Schwann cells
Effectors (muscles and glands)
Toxin neutralisation
Repolarisation
Fatty acids and glycerol
Digestive system (Villi)
Anaerobic respiration/ fermentation (yeast)
ATP
Phagocytosis
Hypothermia
Nephron
Moist surface (Lungs)
Active site
Pathogen
Photosynthesis
Pholoem
Denatured
Cilia and Mucus
Neurotransmitter
Postsynaptic neuron
Kreb's cycle
Bowman's capsule
Antigen
Eukaryotic cell
Passive immunity
Induced-fit & Lock and key theory
Afferent impulses (towards CNS)
ADP + p
Distal convoluted tubule
Hyperpolarisation
Alveoli
Inflammation
Large concentration gradient maintained (Lungs)
Opsonisation
Fish Gills (countercurrent flow)
Glycolysis
Isotonic
acquired immune response (antibody producing B-cells)
Negative feedback systems
Sieve tubes
Memory cells
Loop of Henle
Histamine
Pyruvate
NADPH
TRH
Large SA:V ratio (Lungs)
Synapse
Water potential
Hypotonic
Sieve plates
Electron Transport Chain
Light dependent reactions
Proximal convoluted tubule
Efferent impulses (away from CNS, to the effector)
Sodium influx
Transpiration
Complement system
Antibodies
Sensory neuron
Lysosome (lysozyme)
Osmoregulator
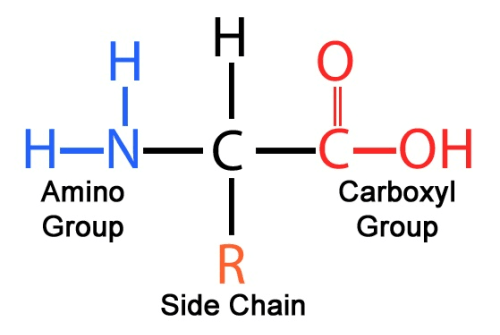
Amino acids
disease vector (e.g. mosquito - carries the pathogen)
Adhesion-cohesion (plants)
Glycoprotein
Hormones
Passive transport
Depolarisation
Threshold potential (neuron)
Sensory receptors (chemo, thermo, photo, mechano, noci)
Axon