
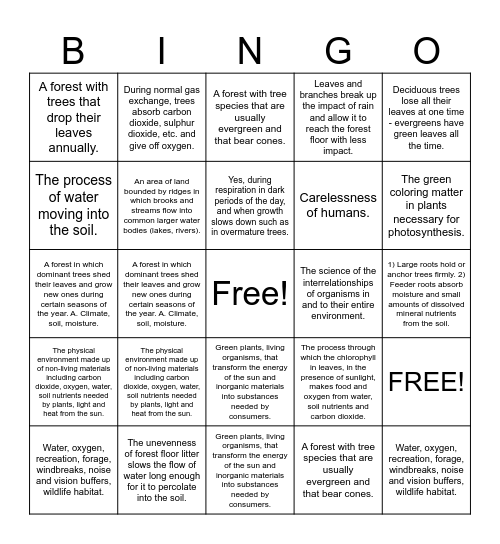
This bingo card has a free space and 49 words: The green coloring matter in plants necessary for photosynthesis., Water, oxygen, recreation, forage, windbreaks, noise and vision buffers, wildlife habitat., Animals which cannot produce their own food and are therefore dependent on producers for food., Green plants, living organisms, that transform the energy of the sun and inorganic materials into substances needed by consumers., The physical environment made up of non-living materials including carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, soil nutrients needed by plants, light and heat from the sun., The fungi and bacteria, primarily in the upper soil layer, that change dead organic matter into basic nutrients for reuse., During normal gas exchange, trees absorb carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, etc. and give off oxygen., Food and shelter., The process of water moving into the soil., The unevenness of forest floor litter slows the flow of water long enough for it to percolate into the soil., An area of land bounded by ridges in which brooks and streams flow into common larger water bodies (lakes, rivers)., Leaves and branches break up the impact of rain and allow it to reach the forest floor with less impact., FREE!, The process through which the chlorophyll in leaves, in the presence of sunlight, makes food and oxygen from water, soil nutrients and carbon dioxide., 1) Large roots hold or anchor trees firmly. 2) Feeder roots absorb moisture and small amounts of dissolved mineral nutrients from the soil., 1) The progressive development of the vegetation toward its highest ecological expression, the climax. 2.) The replacement of one plant community by another., Yes, during respiration in dark periods of the day, and when growth slows down such as in overmature trees., The science of the interrelationships of organisms in and to their entire environment., The process by which water vapor leaves a living plant in the daytime and enters the atmosphere., Deciduous trees lose all their leaves at one time - evergreens have green leaves all the time., A forest in which dominant trees shed their leaves and grow new ones during certain seasons of the year. A. Climate, soil, moisture., A forest with tree species that are usually evergreen and that bear cones., A forest with trees that drop their leaves annually., Carelessness of humans., The first forests developed about 365 million years ago, during the Devonian period., The green coloring matter in plants necessary for photosynthesis., Water, oxygen, recreation, forage, windbreaks, noise and vision buffers, wildlife habitat., Animals which cannot produce their own food and are therefore dependent on producers for food., Green plants, living organisms, that transform the energy of the sun and inorganic materials into substances needed by consumers., The physical environment made up of non-living materials including carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, soil nutrients needed by plants, light and heat from the sun., The fungi and bacteria, primarily in the upper soil layer, that change dead organic matter into basic nutrients for reuse., During normal gas exchange, trees absorb carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, etc. and give off oxygen., Food and shelter., The process of water moving into the soil., The unevenness of forest floor litter slows the flow of water long enough for it to percolate into the soil., An area of land bounded by ridges in which brooks and streams flow into common larger water bodies (lakes, rivers)., Leaves and branches break up the impact of rain and allow it to reach the forest floor with less impact., The process through which the chlorophyll in leaves, in the presence of sunlight, makes food and oxygen from water, soil nutrients and carbon dioxide., 1) Large roots hold or anchor trees firmly. 2) Feeder roots absorb moisture and small amounts of dissolved mineral nutrients from the soil., 1) The progressive development of the vegetation toward its highest ecological expression, the climax. 2.) The replacement of one plant community by another., Yes, during respiration in dark periods of the day, and when growth slows down such as in overmature trees., The science of the interrelationships of organisms in and to their entire environment., The process by which water vapor leaves a living plant in the daytime and enters the atmosphere., Deciduous trees lose all their leaves at one time - evergreens have green leaves all the time., A forest in which dominant trees shed their leaves and grow new ones during certain seasons of the year. A. Climate, soil, moisture., A forest with tree species that are usually evergreen and that bear cones., A forest with trees that drop their leaves annually., Carelessness of humans. and The first forests developed about 365 million years ago, during the Devonian period..
⚠ This card has duplicate items: The green coloring matter in plants necessary for photosynthesis. (2), Water, oxygen, recreation, forage, windbreaks, noise and vision buffers, wildlife habitat. (2), Animals which cannot produce their own food and are therefore dependent on producers for food. (2), Green plants, living organisms, that transform the energy of the sun and inorganic materials into substances needed by consumers. (2), The physical environment made up of non-living materials including carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, soil nutrients needed by plants, light and heat from the sun. (2), The fungi and bacteria, primarily in the upper soil layer, that change dead organic matter into basic nutrients for reuse. (2), During normal gas exchange, trees absorb carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, etc. and give off oxygen. (2), Food and shelter. (2), The process of water moving into the soil. (2), The unevenness of forest floor litter slows the flow of water long enough for it to percolate into the soil. (2), An area of land bounded by ridges in which brooks and streams flow into common larger water bodies (lakes, rivers). (2), Leaves and branches break up the impact of rain and allow it to reach the forest floor with less impact. (2), The process through which the chlorophyll in leaves, in the presence of sunlight, makes food and oxygen from water, soil nutrients and carbon dioxide. (2), 1) Large roots hold or anchor trees firmly. 2) Feeder roots absorb moisture and small amounts of dissolved mineral nutrients from the soil. (2), 1) The progressive development of the vegetation toward its highest ecological expression, the climax. 2.) The replacement of one plant community by another. (2), Yes, during respiration in dark periods of the day, and when growth slows down such as in overmature trees. (2), The science of the interrelationships of organisms in and to their entire environment. (2), The process by which water vapor leaves a living plant in the daytime and enters the atmosphere. (2), Deciduous trees lose all their leaves at one time - evergreens have green leaves all the time. (2), A forest in which dominant trees shed their leaves and grow new ones during certain seasons of the year. A. Climate, soil, moisture. (2), A forest with tree species that are usually evergreen and that bear cones. (2), A forest with trees that drop their leaves annually. (2), Carelessness of humans. (2), The first forests developed about 365 million years ago, during the Devonian period. (2)
Forestry Bowl Questions 1-24 | Forestry Bowl Questions 1-24 | plants | know your science | Matter and Energy in Plants
Share this URL with your players:
For more control of your online game, create a clone of this card first.
Learn how to conduct a bingo game.
With players vying for a you'll have to call about __ items before someone wins. There's a __% chance that a lucky player would win after calling __ items.
Tip: If you want your game to last longer (on average), add more unique words/images to it.