
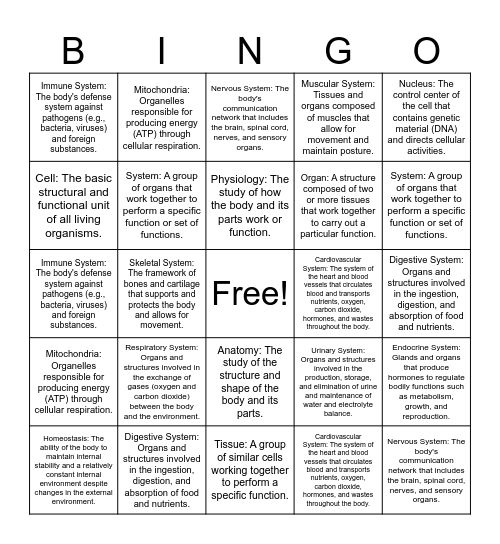
This bingo card has a free space and 39 words: Cell: The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms., Tissue: A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function., Organ: A structure composed of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a particular function., System: A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions., Homeostasis: The ability of the body to maintain internal stability and a relatively constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment., Anatomy: The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts., Physiology: The study of how the body and its parts work or function., Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): The outer boundary of the cell that separates the cell's internal environment from the external environment., Nucleus: The control center of the cell that contains genetic material (DNA) and directs cellular activities., Mitochondria: Organelles responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration., Skeletal System: The framework of bones and cartilage that supports and protects the body and allows for movement., Muscular System: Tissues and organs composed of muscles that allow for movement and maintain posture., Nervous System: The body's communication network that includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory organs., Digestive System: Organs and structures involved in the ingestion, digestion, and absorption of food and nutrients., Cardiovascular System: The system of the heart and blood vessels that circulates blood and transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and wastes throughout the body., Respiratory System: Organs and structures involved in the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the environment., Endocrine System: Glands and organs that produce hormones to regulate bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction., Immune System: The body's defense system against pathogens (e.g., bacteria, viruses) and foreign substances., Integumentary System: The skin and its accessory structures (hair, nails, glands) that protect the body from the external environment and regulate temperature., Urinary System: Organs and structures involved in the production, storage, and elimination of urine and maintenance of water and electrolyte balance., Cell: The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms., Tissue: A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function., Organ: A structure composed of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a particular function., System: A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions., Homeostasis: The ability of the body to maintain internal stability and a relatively constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment., Anatomy: The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts., Physiology: The study of how the body and its parts work or function., Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): The outer boundary of the cell that separates the cell's internal environment from the external environment., Nucleus: The control center of the cell that contains genetic material (DNA) and directs cellular activities., Mitochondria: Organelles responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration., Skeletal System: The framework of bones and cartilage that supports and protects the body and allows for movement., Muscular System: Tissues and organs composed of muscles that allow for movement and maintain posture., Nervous System: The body's communication network that includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory organs., Digestive System: Organs and structures involved in the ingestion, digestion, and absorption of food and nutrients., Cardiovascular System: The system of the heart and blood vessels that circulates blood and transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and wastes throughout the body., Respiratory System: Organs and structures involved in the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the environment., Endocrine System: Glands and organs that produce hormones to regulate bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction., Immune System: The body's defense system against pathogens (e.g., bacteria, viruses) and foreign substances. and Integumentary System: The skin and its accessory structures (hair, nails, glands) that protect the body from the external environment and regulate temperature..
⚠ This card has duplicate items: Cell: The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. (2), Tissue: A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function. (2), Organ: A structure composed of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a particular function. (2), System: A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions. (2), Homeostasis: The ability of the body to maintain internal stability and a relatively constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment. (2), Anatomy: The study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. (2), Physiology: The study of how the body and its parts work or function. (2), Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): The outer boundary of the cell that separates the cell's internal environment from the external environment. (2), Nucleus: The control center of the cell that contains genetic material (DNA) and directs cellular activities. (2), Mitochondria: Organelles responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration. (2), Skeletal System: The framework of bones and cartilage that supports and protects the body and allows for movement. (2), Muscular System: Tissues and organs composed of muscles that allow for movement and maintain posture. (2), Nervous System: The body's communication network that includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory organs. (2), Digestive System: Organs and structures involved in the ingestion, digestion, and absorption of food and nutrients. (2), Cardiovascular System: The system of the heart and blood vessels that circulates blood and transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and wastes throughout the body. (2), Respiratory System: Organs and structures involved in the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the environment. (2), Endocrine System: Glands and organs that produce hormones to regulate bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. (2), Immune System: The body's defense system against pathogens (e.g., bacteria, viruses) and foreign substances. (2), Integumentary System: The skin and its accessory structures (hair, nails, glands) that protect the body from the external environment and regulate temperature. (2)
TEKS 7.13A Functions of Human Body Systems | Body Systems and Cells' Organelles | Body Systems Bingo | Body Systems Bingo | Body Systems part 2 2022
Share this URL with your players:
For more control of your online game, create a clone of this card first.
Learn how to conduct a bingo game.
With players vying for a you'll have to call about __ items before someone wins. There's a __% chance that a lucky player would win after calling __ items.
Tip: If you want your game to last longer (on average), add more unique words/images to it.