
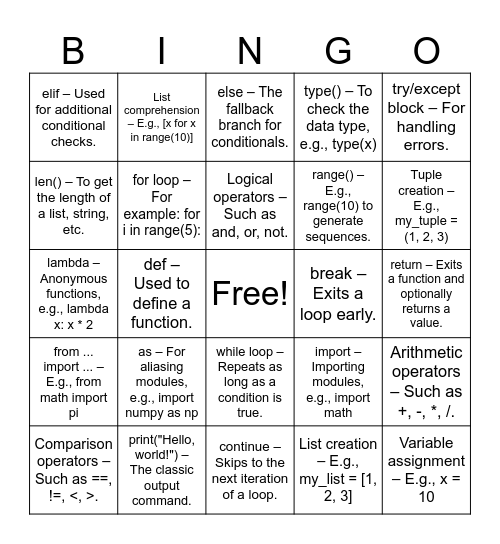
This bingo card has a free space and 30 words: print("Hello, world!") – The classic output command., input() – For getting user input., def – Used to define a function., if – The basic conditional statement., elif – Used for additional conditional checks., else – The fallback branch for conditionals., for loop – For example: for i in range(5):, while loop – Repeats as long as a condition is true., break – Exits a loop early., continue – Skips to the next iteration of a loop., return – Exits a function and optionally returns a value., Variable assignment – E.g., x = 10, List creation – E.g., my_list = [1, 2, 3], Dictionary creation – E.g., my_dict = {"key": "value"}, Tuple creation – E.g., my_tuple = (1, 2, 3), Set creation – E.g., my_set = {1, 2, 3}, import – Importing modules, e.g., import math, from ... import ... – E.g., from math import pi, as – For aliasing modules, e.g., import numpy as np, try/except block – For handling errors., lambda – Anonymous functions, e.g., lambda x: x * 2, f-string – For formatted strings, e.g., f"Hello, {name}", List comprehension – E.g., [x for x in range(10)], range() – E.g., range(10) to generate sequences., len() – To get the length of a list, string, etc., type() – To check the data type, e.g., type(x), Arithmetic operators – Such as +, -, *, /., Comparison operators – Such as ==, !=, <, >., Logical operators – Such as and, or, not. and Docstring – A string literal for documentation, e.g..
CS111 BINGO | CODE VS ANIMATION | 3-15 prog1 (ch 4) | ICS BINGO | Programming Vocab Review
Share this URL with your players:
For more control of your online game, create a clone of this card first.
Learn how to conduct a bingo game.
With players vying for a you'll have to call about __ items before someone wins. There's a __% chance that a lucky player would win after calling __ items.
Tip: If you want your game to last longer (on average), add more unique words/images to it.